How Coffee Grows? Exploring the Journey of Coffee
Coffee, the beloved beverage enjoyed by millions worldwide, has a fascinating journey from its humble beginnings as a seed to the aromatic cup of goodness we savour each day. In this blog post, we delve into the captivating process of how coffee grows, from cultivation to harvest, processing, and beyond. Join us as we embark on a journey through lush coffee plantations, exploring the intricate steps involved in bringing that perfect cup of coffee to your table.
Origins of Coffee:
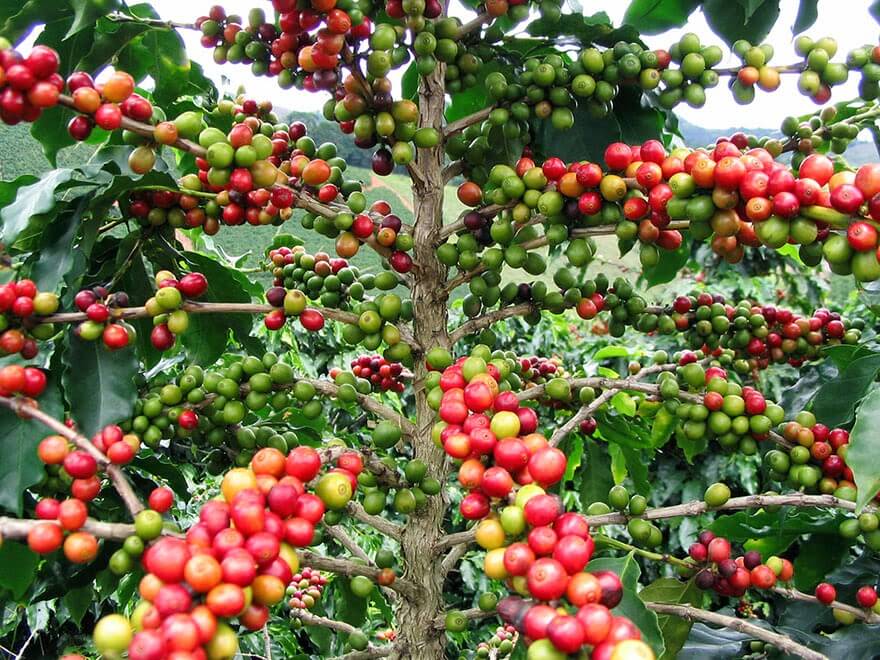
Coffee has a rich history that dates back centuries. Its story begins in the ancient coffee forests of Ethiopia, where the stimulating effects of coffee berries were discovered. From there, the cultivation and trade of coffee spread across the globe, reaching different continents and giving rise to various coffee-growing regions. Today, countries like Brazil, Colombia, Ethiopia, and Vietnam are renowned for their coffee production.
Cultivating Coffee Plants:
The cultivation of coffee begins with selecting the right location and creating favourable conditions for the coffee plants to thrive. Coffee plants prefer tropical climates with consistent temperatures, ample rainfall, and well-drained soils. They are typically grown at high altitudes, which contribute to the development of unique flavors in the coffee beans.
Planting and Growing Coffee:
Coffee plants are usually propagated from seeds in specialized nurseries. The seeds are carefully selected from high-quality coffee cherries. After germination, the seedlings are nurtured in shaded areas until they reach a suitable size for transplantation. They are then carefully planted in the designated coffee fields.
The growing process involves regular maintenance, including pruning, fertilization, and pest control. It takes several years for the coffee plants to mature and produce their first crop. During this time, farmers must provide proper care to ensure healthy growth and optimize yield.
Harvesting and Processing:
Coffee cherries ripen at different rates and are typically handpicked to ensure only the fully ripe cherries are harvested. This selective picking requires skilled labor and is often done multiple times throughout the harvest season.
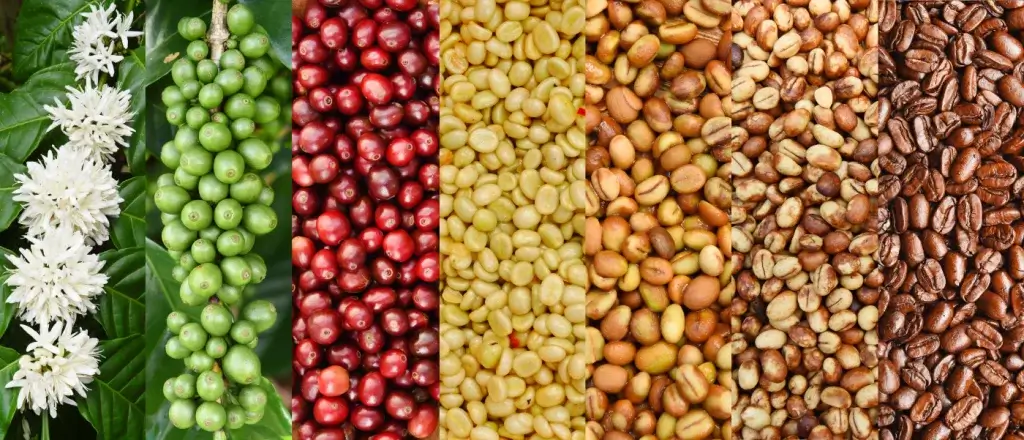
Once harvested, the coffee cherries undergo processing to separate the beans from the fruit. There are two main processing methods: the dry process (natural process) and the wet process (washed process). Each method has its unique characteristics and impacts the flavour profile of the resulting coffee.

Drying and Milling:
After processing, the coffee beans need to be dried to an optimal moisture content. This is typically done by spreading the beans on raised drying beds or using specialized drying machines. Once dried, the beans are hulled to remove the outer layers and reveal the green coffee beans.
Roasting and Packaging:
The green coffee beans are then ready for roasting, a crucial step that transforms them into the aromatic brown beans we recognize. The roasting process involves applying heat to the beans, causing chemical reactions that develop the desired flavours and aromas.
Once roasted, the coffee beans are cooled and packaged to preserve their freshness. They may be sold as whole beans or ground to different sizes, depending on the intended brewing method.
The journey of coffee from bean to cup is a remarkable process that involves careful cultivation, harvesting, processing, and roasting. Each step contributes to the unique flavours and aromas that we associate with our favourite coffee brews. By understanding the journey of coffee, we gain a deeper appreciation for the hard work and dedication of coffee farmers around the world. So, the next time you sip your cup of coffee, take a moment to reflect on the journey it has taken to reach your hands and savour the remarkable flavours that have been cultivated with care and passion.
Disclaimer: This blog post is intended for informational purposes only and does not provide detailed instructions for coffee cultivation. Coffee farming practices may vary depending on the region and specific conditions.